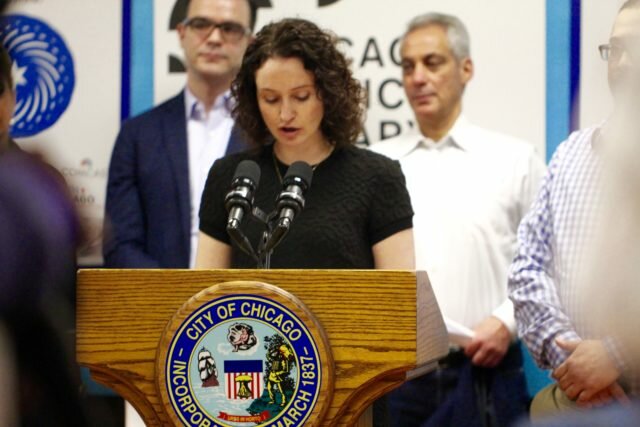
Today we launched Connect Chicago, our initiative to make Chicago the most skilled and connected digital city in America. Following is a roundup of the day.
Here’s the compete text of a press release from Mayor Rahm Emanuel.
MAYOR EMANUEL LAUNCHES CONNECT CHICAGO INITIATIVE TO HELP CLOSE THE DIGITAL DIVIDE IN CHICAGO
Initiative Will Make Digital Skills Training Available at Nearly All Chicago Public Libraries
Mayor Rahm Emanuel and a coalition of public and private partners today launched Connect Chicago — a civic leadership initiative to make Chicago the most skilled and connected digital city in America. Connect Chicago will expand digital skills training throughout the city, and to nearly all Chicago Public Library locations.
“By teaching digital skills, we give Chicago a stronger and more dynamic economy,” Mayor Emanuel said. “Connect Chicago will allow us to expand digital skills training throughout the city and benefit residents of all ages in every neighborhood.”
Connect Chicago will expand digital access and training resources across the city by expanding evidence-based programs in partnership with trusted institutions with a history of serving low-income Chicagoans. Initial investments announced today include the citywide expansion the Chicago Public Library’s CyberNavigator program, which provides computer tutors who help provide access to information resources for adults and youth. The expansion will take CyberNavigators from 48 public library branches to nearly all of the 80 branches across the city, creating an additional 350-400 new training hours per week across Chicago.
“The Library has made it a priority to provide critical tools and resources for adults to learn digital skills,” said Chicago Public Libraries Commissioner Brian Bannon. “This exciting collaborative approach will allow CPL to serve as an access point to digital skills in every neighborhood, through our 80 locations across the city.”
Connect Chicago will also fund the integration of digital skills training into Local Initiatives Support Corporation (LISC) Chicago Financial Opportunity Centers’ programming. Under this investment, LISC Chicago projects to train 1,000 more residents in digital skills during 2016 – 50 percent more than their current capacity. In 2011, LISC Chicago found that patrons who participated in digital skill training alongside other support services at financial opportunity centers were 50 percent more likely to get a job than those that didn’t.
Connect Chicago is the next chapter in Chicago’s commitment to digital access and skills. It is rooted in two recent citywide plans created under Mayor Emanuel’s leadership: the City of Chicago Tech Plan as well as World Business Chicago’s Plan for Economic Growth & Jobs.
“Through investments in coordination, programs, and innovation, we believe Connect Chicago will expand and sustain a thriving digital ecosystem that unleashes Chicago’s economic potential and improves the lives of its residents,” said Jeff Malehorn, President and CEO of World Business Chicago.
Connect Chicago brings together the public and private sectors to focus on neighborhood economic development. Private sector partners include Cisco, Clarity Partners, Comcast, Get IN Chicago, Gogo, The John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, Microsoft, Motorola Mobility Foundation, The Otho S.A. Sprague Memorial Institute, and Sprint. Over the next three years, Connect Chicago aims to raise at least $10 million to strengthen Chicago’s digital foundations and expand this network of programming.
“By bringing these partners together, we are able to do something unique for Chicago,” said Dan X. O’Neil, executive director, Smart Chicago Collaborative. “It allows an unprecedented alignment and coordination of the city’s technology assets.”
“Internet access is important, because it helps kids succeed in school and families participate more fully in their communities and in the economy,” said Matthew Summy, Comcast’s regional vice president of External and Government Affairs. “Comcast is deeply committed to closing the digital divide and to that end in 2011 launched the nation’s largest broadband adoption program for low-income families, Internet Essentials. Since then, nearly 35,000 Chicago families – or about 140,000 individuals – have gained access to the Internet at home through the program.”
“Connect Chicago is a shining example of Chicago’s commitment to digital access and skills,” said Shelley Stern Grach, Director of Technology and Civic Engagement at Microsoft. “We’re proud to be a founding supporter of this innovative initiative to expand 21st century resources across our city.”
For more information on Connect Chicago, visit connectchicago.org.
###
The citywide expansion of CyberNavigators through Connect Chicago builds on the support of the Chicago Public Library Foundation, which has supported the CyberNavigator Program since 1998. There is high demand for CyberNavigator assistance across the city. The expansion will take CyberNavigators from 48 public library branches to over 75 branches, creating an additional 350-400 new training hours per week across Chicago.
Here’s a complete set of royalty-free photos to use in relation to the launch.
Here are posters we used to show the top-level goals, our current investments, and other facts about the program:
Here’s some of the new stories written about the launch:
Emanuel touts plan to expand cyber use in city
By Marwa Eltagouri, Chicago Tribune
In 2013, broadband adoption on home computers and devices was lowest in neighborhoods such as West Garfield Park, Burnside and Brighton Park, as well as other African-American and Latino neighborhoods where poverty rates are high, according to the study. While the majority of people without broadband still connect to the Internet with their smartphones or public computers, the research showed they’re limited in their Internet use and are far less likely to use online courses or access online job applications.
City Launches Connect Chicago Initiative To Expand Digital Skills Training
By Mike Krauser
“It’s not dependent on your zip code, it’s not dependent on your neighborhood, it’s not dependent on your race or income,” Emanuel said. “Everybody will have the access to be part of the 21st century in the sense of what technology is and be conversant.”





















 This morning, Wednesday, March 11, 2015, at 10AM, I will be chairing a
This morning, Wednesday, March 11, 2015, at 10AM, I will be chairing a 
